Email Us
Technical Specifications for Ductile Iron Pipe Joint Types
Flanged joints utilize high-strength bolts (conforming to ISO 898-1 Grade 8.8 or higher) to fasten flange plates on both pipe ends, establishing a rigid connection between upstream and downstream pipelines. Structural loads are entirely borne by the bolts, requiring pressure ratings (e.g., PN16/PN25) matched to the system’s working pressure.This joint type lacks flexible deformation capability and is suited for specialized applications such as valve accessories, cross-material pipeline connections, and detachable pipe sections. Due to limitations in compressibility and weather resistance of thin rubber gaskets (thickness ≤3 mm), sealing efficiency must be optimized by selecting EPDM or PTFE-enhanced gaskets.As the rigid structure cannot absorb axial displacement, pipelines exceeding 50 meters require expansion joints or Ω-compensators (thermal displacement calculated using expansion coefficient α = 0.012 mm/(m·℃)). Flanged joints are unsuitable for subsidence-prone areas. For dynamic load scenarios, transition to K-type mechanical flexible joints (AWWA C111 standard) is recommended. Manufacturing and installation must strictly comply with ISO 7005 specifications for alignment accuracy and torque control.
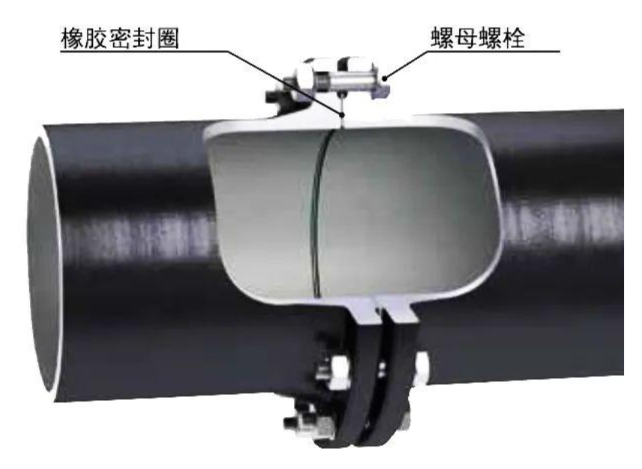

Flexible Joint: A joint capable of providing a certain degree of angular deflection or axial displacement. Includes mechanical flexible joints and push-on flexible joints.Mechanical Flexible Joint: Achieves a flexible connection through mechanical compression devices (such as bolts, clamps) and rubber sealing rings. This allows for limited displacement (axial, radial, or angular) of the pipe while maintaining sealing integrity. Main types include K-Type joints, self-restrained mechanical joints, and clamp-type flexible joints.Push-on Flexible Joint: Relies on the compression of a rubber ring for sealing. Installation is completed simply by pushing the spigot end into the bell end. Characterized by quick installation and allowing for certain displacements, these joints are widely utilized in municipal water supply, drainage, and water transmission projects.
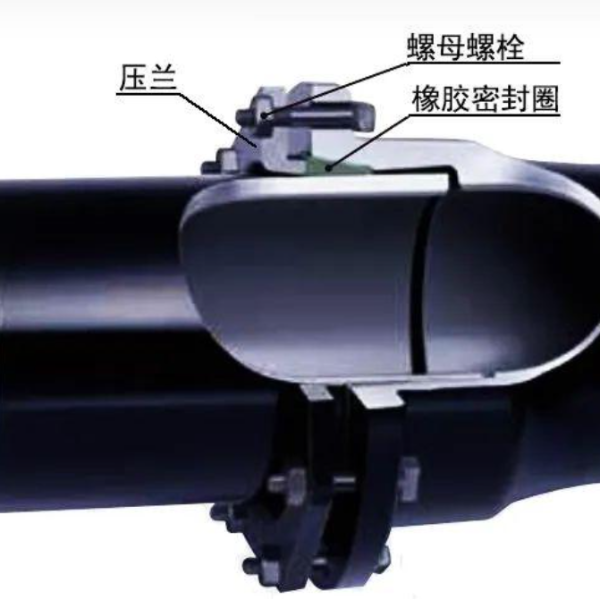
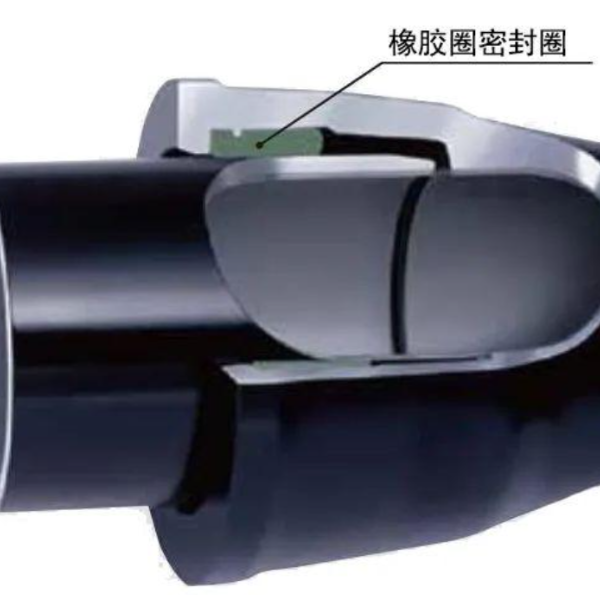


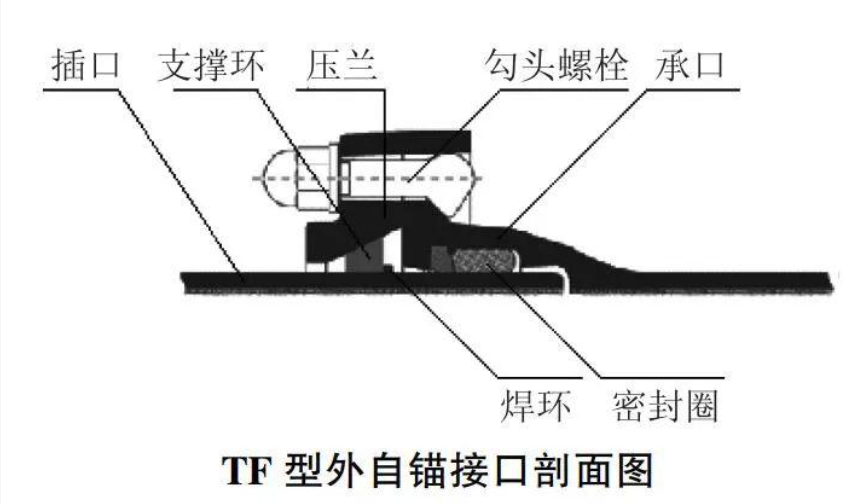
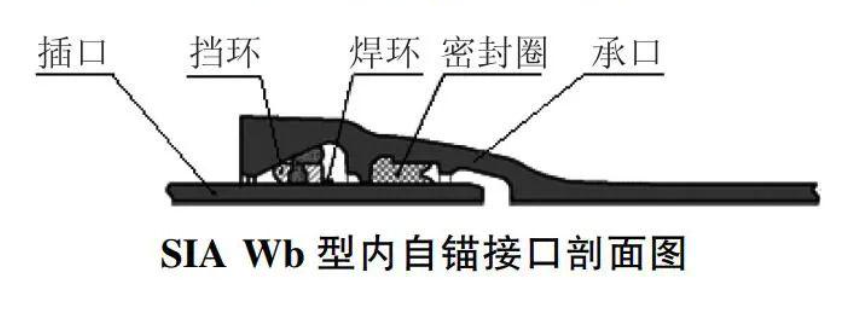
Self-Restraining Joint: A flexible connection technology within Ductile Iron Pipe (DIP) systems designed to resist joint separation. It integrates a mechanical locking device (such as restraining teeth, wedge-shaped locking rings, or anchoring blocks) with a rubber sealing ring. While retaining the displacement compensation capabilities of standard flexible joints (±10mm axial displacement, ±5° angular deflection), it actively counteracts axial pulling forces on the pipeline. This prevents joint separation risks caused by internal pressure, water flow impact, or ground movement.Based on the integrated location of the locking device, self-restraining joints are categorized into two main types: External Self-Restraining and Internal Self-Restraining. Both types provide pullout resistance and flexible displacement compensation. However, they exhibit significant differences in structural design, application scenarios, and installation procedures.
SHANDONG EPOCH EQUIPMENT CO., LTD. is a large-scale professional manufacturer in Shandong Province of China, adheres to the orientation of science and technology, environmental protection, quality and efficiency. At present, it has grown into a trans-regional and multi-industrial enterprise integrating such wide industries as design, development, production and export. Visit our website at https://www.epochpipeline.com/ to learn more about our products. For inquiries, you can reach us at sdepochwater@hotmail.com.
- Why Choose Between UPVC Pipes and HDPE Pipes?
- Why Is Ductile Iron Pipe Still the Safe Choice for Long-Life Water Networks?
- Which Pipeline Installation Machines and Tools Help Me Deliver Faster, Safer, and More Profitable Projects?
- Key points for quality inspection of ductile iron pipes
- Why do Carbon Steel Pipes keep winning tough industrial projects?
- What are the connection methods for ductile iron pipes?
About Us
Contact Us
No. 112, Jiefang Road, Lixia District, Jinan City, Shandong Province, China
Copyright © 2025 Shandong Epoch Equipment Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.













