Email Us
What Makes a Pipe Flange Adapter the Choice for Piping Connections?
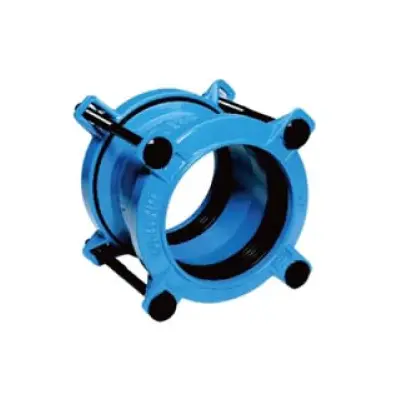
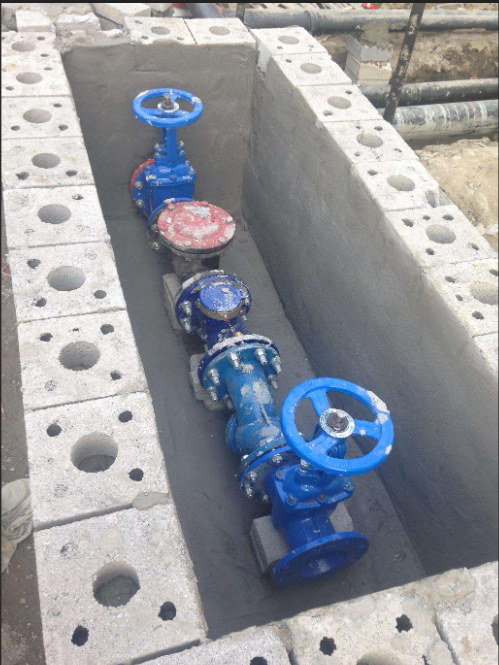
A pipe flange adapter is a critical connector used in piping systems to join flanged equipment or pipelines with different end connections. Instead of relying on welding or threading alone, flange adapters provide a versatile interface that allows secure fastening, disassembly, and maintenance. They are commonly installed in applications where durability, leak resistance, and easy installation are required.
So, what exactly does a pipe flange adapter do?
It serves as a transitional component. One end of the adapter connects to a pipe, while the other end forms a flange that can be bolted to valves, pumps, tanks, or other flanged components. This dual-function design eliminates the need for extensive modifications and ensures compatibility across diverse piping systems.
Pipe flange adapters are manufactured in a variety of sizes, pressure ratings, and materials to accommodate specific system requirements. In sectors like oil and gas, chemical processing, food production, shipbuilding, and water treatment, they are indispensable because they provide a secure, high-performance seal even under extreme operating conditions.
Key Features of a Pipe Flange Adapter:
-
Connection Versatility: Bridges plain-end, grooved, or threaded pipes with flanged components.
-
Pressure Resistance: Withstands varying pressures from low to very high, depending on material selection.
-
Corrosion Protection: Stainless steel, carbon steel, ductile iron, and alloy options extend service life.
-
Easy Maintenance: Detachable design allows quick replacement or inspection without cutting pipes.
Typical Parameters of Pipe Flange Adapters:
| Parameter | Specification Range |
|---|---|
| Nominal Diameter (DN) | DN15 – DN1200 |
| Pressure Rating | PN6 – PN64 / ANSI 150 – 600 lbs |
| Connection Type | Welded, Grooved, Threaded, or Compression End |
| Flange Standard | ANSI, DIN, JIS, BS, EN |
| Material Options | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel (304/316), Alloy, Ductile Iron |
| Surface Treatment | Galvanized, Epoxy Coated, Painted, or Bare Metal |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +450°C (depending on material) |
| Applications | Oil & Gas, Chemical, Water Supply, Food & Beverage, Marine, HVAC |
By combining a standard flange face with a flexible end connection, pipe flange adapters simplify integration across complex systems and reduce long-term operational costs.
Why Pipe Flange Adapters Are Critical in Piping Systems
Why should engineers or contractors choose a pipe flange adapter instead of other coupling methods? The answer lies in the unique balance between strength, flexibility, and convenience.
Compatibility Across Systems
In large-scale projects, it is common to encounter mismatched standards or different pipe-end types. Without an adapter, costly rework or custom fabrication is often required. Pipe flange adapters act as a bridge, ensuring that different systems can be connected safely and reliably.
Reduced Downtime
In industries like oil and gas, downtime translates into massive financial losses. Flange adapters minimize downtime because they allow rapid disassembly and reassembly. When a pump or valve needs inspection, the bolted flange connection can be undone quickly, avoiding complex cutting or welding work.
Cost-Effective Solutions
Instead of replacing entire pipelines or fabricating custom joints, engineers can rely on flange adapters to deliver compatibility. This lowers installation costs and extends the service life of the system.
Safety and Reliability
Pipe flange adapters are designed to withstand high stress, vibration, and extreme temperatures. By ensuring a tight seal, they help prevent leaks of hazardous fluids or gases, which is crucial in chemical and petrochemical industries.
Compliance with International Standards
Most flange adapters are manufactured in accordance with international standards such as ANSI, DIN, JIS, and BS, ensuring global compatibility. This makes them suitable for export projects and multinational installations.
In summary, the reason pipe flange adapters are critical lies in their ability to unify systems, reduce costs, and enhance safety—all while offering a reliable and versatile connection method.
How Pipe Flange Adapters Improve Project Efficiency
The “how” question is central to understanding the real benefits of flange adapters in practical applications. Let’s explore how they directly improve efficiency in design, construction, and operation.
Installation Efficiency
-
Step 1: Align the adapter end with the pipe (weld, groove, or thread).
-
Step 2: Bolt the flange face to the equipment or pipeline flange.
-
Step 3: Apply proper gasket and torque sequence to ensure sealing integrity.
Compared with permanent welds, this process is faster, requires less skill-specific labor, and is reversible.
Maintenance Simplification
A common challenge in piping systems is accessing equipment for maintenance. With welded connections, disassembly requires cutting and re-welding, adding time and cost. Pipe flange adapters eliminate this issue. By simply unbolting the flange, equipment like pumps, filters, and valves can be serviced or replaced.
Scalability and System Expansion
When projects expand, flange adapters make integration simpler. They allow contractors to connect new lines or modify layouts without redesigning entire systems. This flexibility is invaluable for facilities that are constantly upgrading, such as chemical plants or water treatment stations.
Long-Term Cost Savings
The combination of lower installation labor, faster maintenance, and longer service life results in measurable cost savings over the lifespan of a project. This makes pipe flange adapters a strategic investment rather than just a component purchase.
Market Applications and Product Selection Guide
Pipe flange adapters are not one-size-fits-all. Choosing the right one requires understanding system requirements and industry conditions.
Key Industries Using Pipe Flange Adapters
-
Oil & Gas: High-pressure pipelines and offshore platforms.
-
Water Supply & Treatment: Municipal pipelines, desalination plants, wastewater facilities.
-
Chemical Processing: Handling corrosive fluids and aggressive media.
-
Food & Beverage: Hygienic stainless steel adapters for sanitary pipelines.
-
Marine & Shipbuilding: Saltwater-resistant materials and coatings.
-
HVAC & Fire Protection: Quick-install grooved adapters for safety-critical systems.
How to Select the Right Pipe Flange Adapter
-
Determine the Pipe End Type: Welded, grooved, or threaded.
-
Identify Pressure Rating: Ensure compatibility with system pressure.
-
Choose the Right Material: Match media type, corrosion resistance needs, and temperature requirements.
-
Confirm Flange Standard: ANSI, DIN, JIS, or BS depending on project location.
-
Check Surface Treatment: For added durability in corrosive or outdoor environments.
-
Consult Project Specifications: Always verify adapter dimensions and standards with engineering drawings.
By following these guidelines, engineers can avoid mismatches and ensure long-lasting performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Pipe Flange Adapters
Q1: What is the difference between a pipe flange adapter and a coupling?
A pipe flange adapter connects a pipe to a flanged component, while a coupling simply joins two pipes together. Adapters offer greater versatility because they combine a pipe connection with a bolted flange interface.
Q2: Why are gaskets important when using a pipe flange adapter?
Gaskets ensure a leak-proof seal between the flange faces. Without proper gaskets and torqueing, leaks may occur even if the adapter itself is high quality.
Q3: Can a pipe flange adapter handle both high and low temperatures?
Yes, depending on the material. Stainless steel and alloy adapters can withstand high temperatures up to +450°C, while ductile iron or coated steel versions are suitable for moderate conditions.
Pipe flange adapters are more than just connectors—they are the backbone of efficiency and safety in modern piping systems. By bridging different pipe ends and flanged equipment, they save time, reduce costs, and provide long-term reliability across industries. From oil and gas to water treatment and marine applications, these components play a vital role in ensuring smooth operations.
At Epoch, we take pride in delivering high-quality pipe flange adapters engineered for performance, durability, and global standard compliance. Whether you are upgrading existing infrastructure or developing a new project, our products provide the trusted solution you need.
For more details, technical consultation, or to request a quote, contact us today and discover how our flange adapters can add value to your next project.
- Why Choose Between UPVC Pipes and HDPE Pipes?
- Why Is Ductile Iron Pipe Still the Safe Choice for Long-Life Water Networks?
- Which Pipeline Installation Machines and Tools Help Me Deliver Faster, Safer, and More Profitable Projects?
- Key points for quality inspection of ductile iron pipes
- Why do Carbon Steel Pipes keep winning tough industrial projects?
- What are the connection methods for ductile iron pipes?
About Us
Contact Us
No. 112, Jiefang Road, Lixia District, Jinan City, Shandong Province, China
Copyright © 2025 Shandong Epoch Equipment Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.